Piston
- 2011-12-08 22:46:26
-

Engine pistons are one of the most complex components among all automotive or other industry field
components. The engine can be called the heart of a car and the piston may be considered the most
important part of an engine
Piston terminology
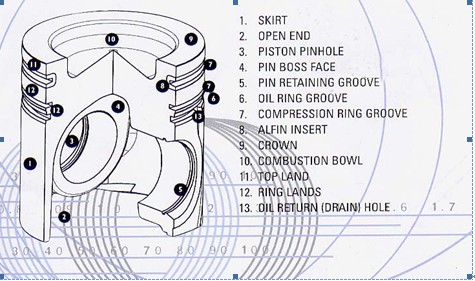
Pistons working conditions and performance requirements
Pistons working conditions:
* Moment of the explosion engine combustion chamber, the gas temperature can reach 2000 ℃ -2500 ℃, the temperature of the piston head is generally not less than 200 ℃;
* Top of the gas under pressure, the pressure for maximum power stroke, gasoline engine up to 3 ~ 5MPa, diesel engines up to 6 ~ 9MPa (standard atmospheric pressure of 0.1MPa);
* High-speed (8 ~ 12m / s) reciprocating motion, and the speed is constantly changing;
* Deformation and accelerated wear, and chemical corrosion by the gas.
Piston performance requirements:
* Have sufficient stiffness and strength, power transmission and reliable;
* Thermal conductivity and good resistance to high pressure, high temperature, wear-resistant;
* Quality, small, light weight, minimize reciprocating inertia force.Shape of the piston structure
■ Piston top
★ sharp : Flat head, Cup head,Home head,Hump head,Contour head and etc
Flat head
The top is a flat, simple, easy to manufacture, heat a small area, at the top of the stress distribution is more uniform, generally used in gasoline, the diesel engine is rarely used.
Cup head
Top was shaped depression, pit shape and position must be conducive to the burning of combustible mixture, a double vortex pits, ball pits, U-shaped pits and so on. Used for diesel engines.
Home head
Was raised dome-shaped, its top strength, from the guide will help to improve the ventilation process, two-stroke gasoline engine (motorcycles) often use dome pistons.
valve relief
primarily for the valve to provide sufficient ,Enough space, so that the smooth intake and exhaust
★ Work Environment:
* Moment of the explosion engine combustion chamber, the gas temperature can reach 2000 ℃ -2500 ℃;
* Top of the gas under pressure, the pressure for maximum power stroke, gasoline engine up to 3 ~ 5MPa, diesel engines up to 6 ~ 9MPa;
* Deformation and accelerated wear, and chemical corrosion by the gas.★ Function:
*Bear the Pressure
* Composition of the combustion chamber■Piston Design features
1 have sufficient mechanical strength and stiffness.
2 can effectively block the heat reached the piston head.
3 high-temperature corrosion resistance.■ Piston Process
1.hard-anodized surface treatment:
It is the piston at the top of a layer of aluminum into high-density alumina, the thickness of at least 0.1 mm, maximum resistance to wear the piston; cold-start prevents the piston due to thermal shock and thermal stress caused by high and possible cracking.2.electron beam welding:
Piston top and skirt in some vacuum electron beam welding instead of screws. Welding can be done after appropriate heat treatment. Turbocharged diesel engine pistons for high, but not all materials can be welded.3.Diffusion bonding method
Can best thermal expansion, tensile cylinder, wear and maximum thermal performance can be split into account, does not increase the weight and cost. During the diffusion bonding layer is formed between two metal atoms penetrate, bond strength equal to or more than their parent metals. W63 and HID100 top aluminum can be used as materials.Piston head features
1 Install piston rings
2 seal: together with the piston cylinder seal to prevent leakage of combustible gas mixture to the crankcase
3 Heat Transfer effect: the (70 ~ 80) percent of the heat to pass through the piston cylinder wallPiston head design features
Design keypoint
1 have sufficient mechanical strength and stiffness.
2 to ensure high operating temperature, however, a small temperature difference.
3 dimensions as compact as possible, in order to reduce the weight of the piston.Piston head technology
1 drill hole:
Bottom surface of the oil ring in a number of radial holes drilled so that the oil rings were scraped from the cylinder wall through the holes back into the oil sump.
2 insert wear ring:
the first ring groove at the (sometimes including a second ring groove)
High wear resistance of austenitic cast into a nickel-iron ring.
3 into heat in the combustion chamber throat guard:
In order to solve the piston head crack.
4 In the first ring groove above the tank car insulation:
So that part of the heat load shunt.Knowledge:
◎ piston ring groove wear performance of great impact. Such as ring groove
Wear ranging from the piston ring groove on ran back and forth, causing gas
Tank leak, affecting engine power, while in the piston ring derailment,
Cause engine damage (cylinder). In order to extend the life of the piston,
Pay special attention to improve the wear resistance of the first ring groove.◎ nickel with high wear resistance, it was used as the Ring of material,
Methods and piston Ring similar process to the form of atomic diffusion.
The finished product must ensure that the bond rate of 85%.
The ultrasonic testing and other testing methods.Piston skirt
Skirt structure:
1 <skirt of the piston oil ring groove from the first end until the next part of the bottom of the piston, which includes the loading piston pin pin hole;
2 <piston pin bore a very high precision (high precision reasons), making thick;
3 <Circlip: some end pin seat hole near outer ring at a card slot, limiting the piston pin to traverse. Some non-ring, piston pin hole in the piston is interference fit, heat the piston during installation, and then stuffed into the corresponding piston pin position.The reasons of pin hole for high precison
Mainly refers to the floating piston pin and the pin hole with precision. If the gap is too large, the work will have a relative motion caused by the additional impact of the gap is too small, it is difficult to ensure that normal lubrication and cause the piston pin killed. Piston pin and pin seat with the gap as follows:
Pin hole diameter
(mm)
25
50
75
100
gap (micron) 3~4
6~8
9~12
12~16
Piston skirt design features
1 connecting rod can withstand lateral pressure generated by the swing
2 ensure a good oriented
3 area with sufficient pressure to form a good Return Home] [Print] [Go Back] Next
- Piston
- Bedford
- BMW
- Catterpillar
- Cummins
- Daewoo
- Daf
- Daihatsu
- Deutz(K.H.D)
- Fiat/iveco
- Ford
- Hino
- Honda
- Hyundai
- Isuzu
- John deer
- Kamaz
- Kia
- Komatsu
- Landrover
- Liebherr
- Lister
- Lombardini
- Mack
- Man
- Mazda
- Mercedes Benz)
- Mitsubishi
- MTZ (Belarus)
- MWM
- Nissan
- Opel
- Perkins
- Peugeot
- Renault/RVI
- Scania
- Steyr/Howo
- Suzuki
- Toyota
- Volvo
- VW
- Yanmar
- Zetor
- Piston ring
- ASIA
- Bedford
- BMW
- Caterpillar
- Chrysler
- Cummins
- Daewoo
- Detroit
- Daf
- Daihatsu
- Deutz (KHD)
- Fiat/Iveco
- Ford
- Hino
- Honda
- Hyundai
- Isuzu
- John Deere
- Kia
- Komatsu
- Man
- Mazda
- Mercedes-benz
- Mitsubishi
- Nissan
- Opel
- Perkins
- Peugeot
- Renault/RVI
- Saviem
- Scania
- Steyr
- Subaru
- Suzuki
- Toyota
- Volkswagen
- Volvo
- Yanmar
- Marine
- Air compressor
- Cyliner Liner
- Gasket kits
- Engine bearing
- Engine head & block
